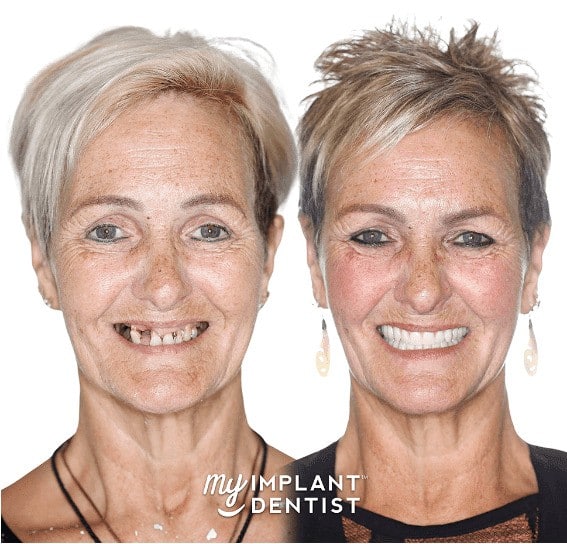
Contents
KEY TAKEAWAY
- There are two types of gum disease: Gingivitis and Periodontitis.
- The most common symptoms of gum disease are swelling and bleeding of the gums, particularly when brushing or flossing.
- Early detection is the most effective method of treatment for gum disease.
- Maintaining good oral hygiene is essential to prevent gum disease.
- Gum disease affects over 30% of adults in Australia.
- The primary cause of gum disease is the accumulation of bacteria near the gum, known as plaque.
- The symptoms of gum disease do not manifest until the condition has progressed significantly.
- Poor oral hygiene, smoking, hormonal changes, illnesses, genetics, certain medications, and poor nutrition can increase the risk of gum disease.
- The first stage of gum disease is gingivitis, which is caused by plaque buildup on the teeth.
- If gingivitis is left untreated, it can progress to mild periodontitis, which involves receding gums, bone loss, and small pockets forming between gums and teeth.
Gum disease affects over 30% of adults in Australia. It is a very common oral disease, although it is less common in children.
One of the primary symptoms of gum disease is bleeding. The gum becomes swollen and begins to bleed when you brush them.
Gum disease is a tricky oral health problem. The symptoms can be deceiving. If you discover the early signs and symptoms you experience in your gum area.
Frequent dental check-ups can help to set things right.
Keep reading this article, where we show you exactly all you need to know about gum disease, how to treat it, and how to get yourself on the safer side.
What Is Gum Disease?
Gum disease, also known as periodontal disease, is a common oral health condition that affects the tissues surrounding and supporting the teeth. It’s characterised by inflammation, soreness, or infection of the gums. If left untreated, gum disease can lead to severe complications, including tooth loss. Regular dental check-ups and maintaining good oral hygiene are crucial in preventing and managing gum disease.
Gum Disease Causes
Gum disease is primarily caused by plaque, a sticky film of bacteria that continuously forms on our teeth. When plaque is not effectively removed by regular brushing and flossing, it can irritate the gums, leading to gum disease. Certain lifestyle factors, such as smoking, poor nutrition, and high stress levels, can increase the risk of developing gum disease. Additionally, certain diseases, such as diabetes, can make individuals more susceptible to gum disease.
Stages Of Gum Disease
Gingivitis
The very first phase of gum disease is gingivitis. It is inflammation of the gums due to excess plaque on the teeth.
Plaques are a deposit of food germs and particles on your teeth. There is always a build-up of bacteria in your teeth, but they become harmful when conditions allow them to increase quickly.
You risk developing gingivitis if you don’t practice good oral hygiene daily. One of the earliest symptoms of this stage of gum disease is bleeding when brushing or flossing the teeth.
Periodontitis
When left untreated, gingivitis can turn into mild periodontitis. In the early stages of periodontitis, the gums start to recede from your teeth, and small pockets begin to form between your gums and teeth. You also start losing some bones around the gum area.
This mild stage of gum disease results in plaque, bacteria, and tartar being trapped in areas your toothbrush and floss can’t reach.
The gum disease now progresses to moderate periodontitis. At this stage, you lose more bone around your teeth. Bacteria destroy the soft tissues that support your teeth. Your gums become sore and tender.
There may also be an inflammatory response throughout your body. Bleeding and pains become more common at this stage.
Progress is made, and it advances to severe periodontitis. In the late stage of periodontitis, bone loss continues, and your teeth may become loose and begin to fall out.
Your gum line becomes infected and filled with pus in addition to bleeding, which can result in persistent bad breath (halitosis).
Signs & Symptoms Of Gum Disease
Gum disease progresses slowly, and the most obvious signs manifest in the late stages. The indicators of gum disease include:
- Swollen and bleeding gums during and after brushing.
- Persistent bad breath in the mouth.
- Reddish or purplish gums
- Tooth loss
- Pus around the gum line
- Inflammatory responses throughout the body
- Foul taste in your mouth
- New gaps developing between your teeth
- Gums that pull out from the teeth
- Changes in how the teeth fit when you bite
- Pain when chewing
Diagnosis of Gum Disease
Your dentist can detect the early symptoms of gum disease in a routine check-up or dental examination. Your dentist can monitor your periodontal status over time to ensure it doesn’t get worse. This is why a routine check-up at your dentist is necessary.
Your dentist will check for swelling, firmness, pocket depth, and gum bleeding during a dental examination. Your dentist might measure any pockets on your gums using a probe or a tiny ruler. In most cases, this test is painless.
The dentist further checks for teeth sensitivity, movement, and appropriate tooth alignment. They may also give you a professional clean if plaque and tartar are on your teeth.
Another excellent option for diagnosing gum disease is a dental x-ray. Sometimes, your dentist will direct you to a periodontist, considered one of the top experts in managing and treating gum disease.
Treatment of Gum Disease
Gum disease treatment aims to inhibit the spread of the condition and encourage the reattachment of healthy gums to teeth. The treatment aims to reduce the depth of pocketing, swelling, and infection risk.
The treatment option chosen by your dental care provider depends on your disease stage, overall health, and response to previous treatment. There is a surgical and non-surgical treatment for gum disease.
In most cases, your dentist will suggest you get a root scale & clean treatment. If the gum disease stage is at severe periodontitis, you must visit an emergency dentist and treat it urgently.
However, it is not advisable to wait till the disease is at the severe stage before you go to your dentist for treatment.
Gum Disease Treatment Cost
The cost of gum disease treatment in Australia varies based on the severity of the condition and the type of treatment required. Basic treatments like professional cleaning and scaling can cost from $1,000. More advanced treatments, such as surgical procedures, can range from AUD $1,000 to $3,000.
However, specific costs depend on your dental clinic. My Implant Dentist charges affordable fees for all our treatments and consultations.
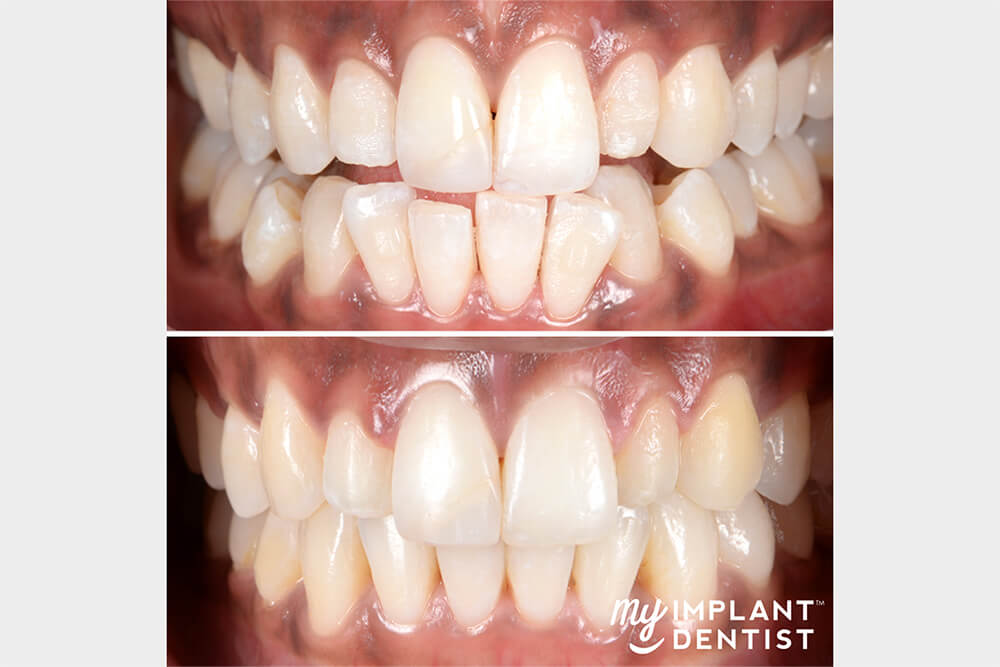
When Should I See My Dentist?
If you notice gum disease symptoms, such as reddish or bleeding gum, visit your dental care provider immediately. Regaining control of your dental health requires quick action. The longer you wait, the worse it becomes and the more extensive treatment it will require.
Complications
Complications that arise from gum diseases treatment include:
- A loose tooth may fall out or require extraction.
- Increased risk of respiratory disorders, heart disorders, and diabetes
- Complications during pregnancy are more likely, which include low birth weight and preeclampsia
- Receding gums
- Painful abscess
How To Treat Gum Disease
Treatment of gum disease is effective using surgical and non-surgical methods. The best way to treat gum disease is to get a professional clean immediately.
Your dentist will professionally clean your teeth to remove the plaque and tartar. They will also polish the teeth and treat them with fluoride.
Non-surgical treatment options work best for gingivitis and mild to moderate periodontitis. The following procedures are effective:
- Your dentist may prescribe some oral antibiotics to fight the infection. Sometimes, topical antibiotics under the gums can help the affected region.
- Deep scaling, cleaning, and root planning are efficient methods of treating gum disease.
Surgical methods are effective in moderate and severe periodontitis. Some surgical treatments include flap surgery, bone grafting, gum graft, and guided tissue regeneration.
FAQs
What Is the Best Treatment For Gum Disease?
Topical and oral antibiotics, root scaling, and bone grafting are one of the various ways to best treat gum disease.
How Long Is Treatment For Gum Disease?
The treatment takes about 2-3 weeks but depends on the severity of the gum disease.
Can Dentists Rebuild Gums?
While your gums can’t regrow, your dentist can use surgical treatment to replace the missing tissue and restore your appearance and oral health.
Does Salt Water Help Gums?
Yes, it helps reduce inflammation and swelling in the gums.
Why Are My Gums Receding So Fast?
Poor oral hygiene is a factor for your gums receding so fast as it builds up tartar which in turn breeds disease-causing bacteria, causing a receding toward the root.
What Is The Quickest Way To Heal Receding Gums?
For your receding gums to heal faster, use the following: Saltwater rinsing, oil pulling, green tea, and maintaining good oral hygiene.
Conclusion
Gum disease can affect anybody, especially adults. If you are not careful enough to treat it early, the disease will worsen.
While getting early treatment, you should never treat the infection at home. Ensure you visit a qualified dental clinic to get your teeth checked.
If you are in Perth, you should visit My Implant Dentist, where our skilled dentists will check your teeth and recommend suitable treatment options for you. Contact us now to book an appointment.