Contents
Key Takeaways:
- The abutment is the “connector” between the tooth implant and the artificial tooth.
- It shapes and tightens the gum tissue and prevents food from settling around the implant.
- The abutment can be fragile, so avoid rinsing, spitting, or touching the wound on the day of surgery.
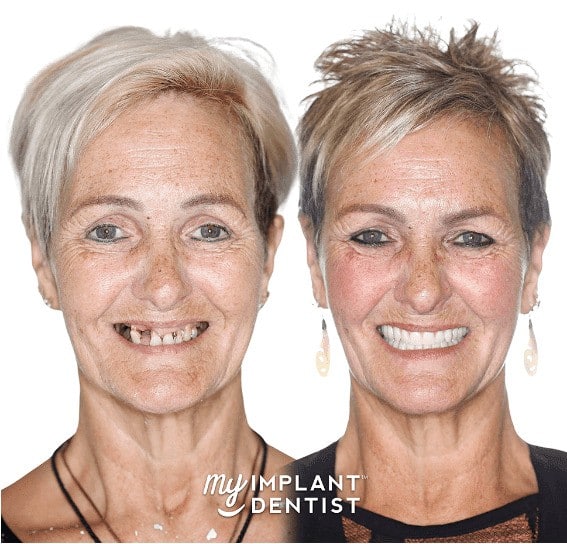
A dental abutment is connected to a dental implant. It is a major component in fitting a dental implant to the jaw. Abutments can also be used to speed up the healing process of gum tissue.
If you’re going for replacement teeth and interested in knowing what an abutment is and its purpose in your mouth, keep reading this article.
What is a Dental Implant Abutment?
The metal part that serves as a foundation for a crown is called an abutment. An abutment functions as a connector; one part is attached to your jawbone, while the crown is fitted on the other end.
After you recover from your operation, your dentist will attach the abutment, which is a metal link, to your dental implant. The abutment firmly holds your crown and fastens it to the implant.
If you have a dental bridge, two abutments will receive crowns, which pontics will join. Pontics are other replacement teeth that sit on top of your gums.
The use of abutment in any procedure is done with local anesthesia. Abutments can be made of Zirconia, gold, stainless steel, titanium, or polyether ether ketone.
What Is the Purpose of Abutments?
The abutment connects the tooth implant and the artificial tooth. The tooth implant can be the crown, bridge, or denture.
Dental implant abutments are used in restorative dentistry and are sometimes called prosthetic implant abutments.
Ceramic abutments are not as strong as metal abutments. But they are used to enhance the appearance of the prosthesis by blending seamlessly with the prosthetic tooth.
The general purpose of an abutment is to provide a base for the functional restoration of bites and the restoration of beautiful smiles.
What Are The Different Types of Abutments For Dental Implants?
1. Prefabricated
Manufacturing companies usually produce prefabricated abutments, and they come in various sizes and shapes. The prefabricated abutment is also known as a stock abutment.
They can be made from Zirconium, gold, titanium, and surgical stainless steel. Titanium abutments are popularly used because of the excellent properties of titanium alloys. They have good strength and biocompatibility.
The zirconium abutment is the most recently used to complement the aesthetics of dental implant Brisbane restoration.
2. Custom Made
The custom-made abutments are made at the dental laboratory after the dentist takes an impression of the top of the implant made with the adjacent teeth.
The abutment is unique to the patient and designed to take the form of the missing natural tooth. Custom abutments are created to fit the gum and soft tissue contours while being compatible with the crown of a natural tooth.
The abutment can then be made of zirconia, titanium, or titanium anodised to a gold colour. They are a more suitable fit for your teeth. The impression taken of your mouth is used to create an abutment that matches the angle, shape, and size of your mouth.
Custom abutments are much more expensive than stock or prefabricated abutments. However, they have better aesthetics.
How Are Dental Abutments Placed?
1. Place the Implant
Once the dentist has fixed the implants, the next step towards placing the dental abutment is to expose the implant.
A second surgery is made to place the abutment. Your dentist makes a small incision on your gum tissue.
2. Digital Abutment & Crown Design
This is where the dentist takes note of the choice of abutment to use. If you are going for a custom-made abutment, your dentist takes an impression of your mouth to make one that matches your mouth’s shape and profile.
3. Place Healing Abutments
A temporary abutment known as a healing abutment is secured to the implant. Healing abutments are called healing caps, and they aid in recovering the gum tissue surrounding the implant site.
The final abutments are placed after gum healing so that the prosthesis and implant can be connected.
4. Place Final Abutments
Your dentist places the final abutment when the gums have healed.
Note: Abutments may be implanted alongside the implant (1-stage surgery). Or, after implant placement, they could be put in during a subsequent procedure (2-stage surgery).
What To Expect After The Procedure?
The healing process for gums around abutments typically takes 4 to 6 weeks.
After the surgery, follow your surgeon’s recommendations for what meals to eat throughout that period.
Your dentist will give you directions on how to clean the area around the abutments. Cleaning properly helps to heal and prevents infection. Ensure you adhere strictly to all instructions from your surgeon to avoid complications.
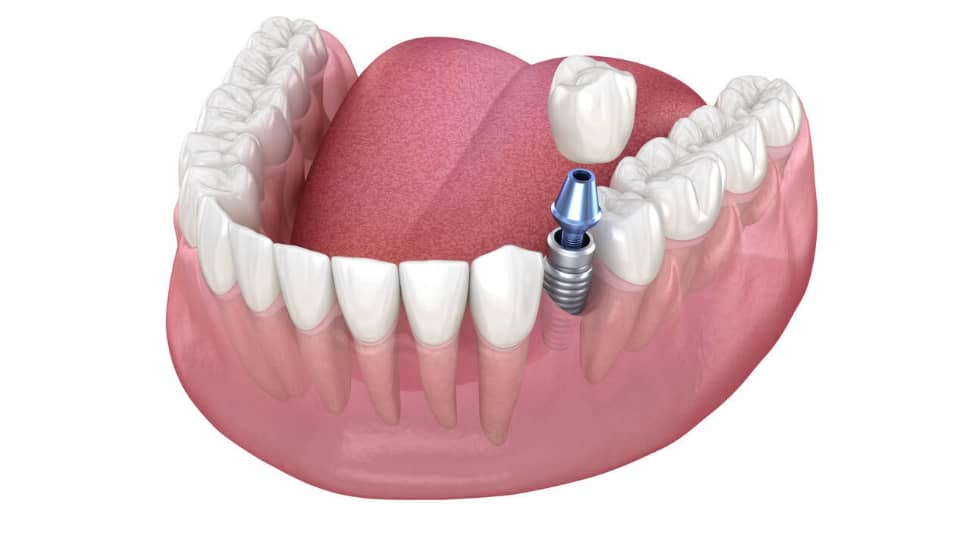
How The Crown Is Connected To the Abutment
Your dentist can use either of the two methods below to attach the crown to try abutment: Use a tiny screw (called screw-retained dental crowns) or use dental cement (called cemented crowns).
The Screw Retained Dental Crowns hold abutments and crowns firmly in place while making replacement and repair simple without harming neighbouring components. They are easy to replace and are not suitable for front-row teeth.
The screw-retained crown is more suitable for the teeth towards the rear of the mouth.
The Dental Cement is bonded to the abutment using special dental cement. They are aesthetically pleasing and cosmetically appealing though the repair and replacement are harder.
When cemented crowns fail, the dentist should take out the entire crown and replace them. For many patients, seeing crowns with screws may be upsetting. For the teeth in the front row, cemented dental crowns are the best option.
Benefits of Using A Healing Abutment
- A healing abutment also called a healing cap or gingival former helps to promote tissue healing (hard and soft) around the implant.
- It also protects the main cap of the implant from accumulating debris and plaque.
- It shapes and tightens the gum tissue and prevents food from settling around the implant.
How Can I Care for Abutments?
- You must gently but thoroughly rinse the area around your healing abutment as soon as you can see it. Do this every morning with the prescribed antibacterial mouthwash from your surgeon.
- The day after your surgery, you are permitted to brush your teeth. But you must avoid brushing the gums or the healing abutment.
- In the third and fourth week after your surgery, you may now gently wipe the healing abutment 2-3 times per day using some cotton dipped in the antimicrobial mouthwash.
- All day long, keep rinsing with salt water. Food and plaque should come away without the need for vigorous scrubbing or wiping.
- From the fifth week after your surgery, you can now brush your abutment but do so gently. Do not scrub hard, as you may hurt your gum tissue and implant. Check out, how to take care of dental implants to learn more!
faqs
What Should I Do After Abutment Surgery?
Avoid rinsing, spitting, or touching the wound on the day of surgery. Also, avoid chewing until the numbness from the anesthetic has worn off.
How Long Does It Take For Dental Abutment To Heal?
Dental abutments take four to six weeks to heal.
How Long After Implant Can I Place Abutment?
One to two weeks after implants, your dentist will place the abutment.
What Should I Eat After Abutment Healing?
You can eat potato mash, yogurt, scrambled eggs, mashed banana, protein shakes, and Applesauce.
Is Abutment Surgery Painful?
It is little, or no pain felt in placing the abutment.